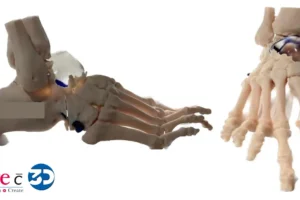
Imagine a world where surgeons operate with a precise, 3D replica of your unique anatomy in hand. This isn’t science fiction – it’s the reality of 3D printing in healthcare. This innovative technology is transforming surgical planning and patient care, offering a new level of customization and precision.
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, represents a revolutionary advancement in technology that creates three-dimensional objects by layering materials based on digital models. This innovative process has found a significant foothold in various industries, and its impact on healthcare has been particularly profound. In the medical field, 3D printing has evolved from theoretical applications to practical implementations that enhance surgical precision and patient outcomes.
The origins of 3D printing in healthcare can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began experimenting with the creation of anatomical models derived from a patient’s imaging data. These early applications paved the way for further exploration into bioprinting, which involves the creation of tissues and organs using living cells, thus shifting the paradigm of traditional medical practices. Over the years, the technology has expanded to produce customized implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments, allowing for tailored solutions that cater specifically to individual patient needs.
One of the most significant aspects of 3D printing in healthcare is its ability to produce complex geometries and intricate designs that would be difficult, if not impossible, to achieve using conventional manufacturing methods. For instance, orthopedic surgeons can utilize 3D surgical planning and 3D-printed models of bones to better plan and execute surgeries, drastically improving the accuracy and success rates of their procedures. This approach enables surgeons to rehearse operations, anticipate challenges, and develop strategies to mitigate risks, ultimately fostering a higher degree of confidence during surgery.
As 3D printing technology continues to advance, its applications within the healthcare sector are expanding, yielding innovative solutions that enhance both planning and execution of surgical procedures. This transformative force is not merely a technological trend; it is paving the way for a new era in medicine, where personalized care becomes the norm rather than the exception.
Table of Contents
From Generic to Personalized: The Rise of 3D Printed Implants
Traditionally, implants were one-size-fits-all. This could lead to complications and a less than optimal fit. 3D printing allows for the creation of custom implants, perfectly tailored to each patient’s anatomy. This leads to several advantages:
- Improved Fit and Function: Customized implants reduce the risk of rejection and ensure better functionality.
- Reduced Surgical Time: Pre-made implants fit seamlessly, minimizing operation time and recovery periods.
- Enhanced Patient Outcomes: Personalized implants can lead to better long-term results and a faster return to normalcy.
The Evolution of Surgical Planning
Traditional surgical planning methods have long been a cornerstone of medical practice, utilizing two-dimensional images such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs to guide surgeons in their preparations. While these imaging techniques offer valuable insights into patient anatomy, they inherently present limitations, particularly when it comes to complex cases. The reliance on flat images can obscure critical spatial relationships and anatomical details, making it challenging for surgeons to fully visualize the intricacies of individual cases. Additionally, the interpretation of these images can vary widely among practitioners, introducing an element of subjectivity that can affect surgical outcomes.
To enhance surgical planning, surgeons often utilize physical models created from imaging data. However, traditional modeling techniques are either time-consuming or lack the fidelity needed to accurately represent the patient’s unique anatomy. Furthermore, these models often cannot replicate the dynamic nature of human tissues and organs during actual surgical procedures. As a result, the surgical team may approach a procedure with a generalized understanding, rather than a tailored strategy built on precise anatomical representations.
Enter 3D surgical planning and 3D printing, a groundbreaking technology that has radically transformed the landscape of surgical planning. This innovative approach allows for the creation of accurate, patient-specific anatomical models, using materials that closely mimic the properties of human tissues. The integration of 3D surgical planning and 3D printing into surgical planning not only addresses the limitations of traditional methods but also enhances precision and personalizability. Surgeons can physically interact with these models, examining them from every angle, and devising strategies that are uniquely suited to each patient’s condition. This shift toward three-dimensional visualization and modeling marks a significant advancement in the field, promoting better preoperative preparation and improving surgical outcomes.
3D surgical planning and 3D printing for Patient-Specific Models
Advancements in 3D printing technology have allowed the creation of patient-specific anatomical models that are transforming surgical planning. These models are produced using precise imaging techniques such as CT or MRI scans, which generate high-resolution data of a patient’s unique anatomy. Once the data is processed, it is translated into a comprehensive 3D replica of the specific body part or organ, enabling surgeons to visualize and manipulate the model before performing actual procedures.
The primary benefit of utilizing these anatomical models lies in their ability to enhance surgical accuracy. By having a physical representation of the patient’s anatomy, surgeons can better understand the complexities involved in a particular case. This level of understanding allows for meticulous preoperative planning, as surgeons can practice the surgical procedure on the 3D model. Consequently, this preparation leads to more informed decision-making during surgery, which can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Moreover, the use of patient-specific models also contributes to reducing intraoperative risks. With a better grasp of the patient’s anatomy, surgeons can anticipate potential complications and adjust their techniques accordingly. For instance, these models can highlight critical structures that need to be preserved or avoided during surgery, thereby minimizing the possibility of damage to healthy tissue. Additionally, the ability to simulate different surgical approaches on the model further enhances the likelihood of a successful operation.
Overall, 3D surgical planning and 3D printing technology presents an innovative approach to developing patient-specific models that not only streamline surgical planning but also enhance the precision of surgical interventions. By yielding a tactile, accurate representation of a patient’s unique anatomy, 3D printing is poised to reshape the landscape of modern surgery, resulting in improved patient care and outcomes.
Beyond Implants: 3D Printing’s Diverse Applications
3D printing’s impact goes beyond implants. Surgeons can now utilize 3D printed:
- Anatomical Models: These realistic replicas of a patient’s organs or bones allow for better preoperative planning, improved communication between surgeons and patients, and more efficient training for medical professionals.
- Surgical Guides and Instruments: Custom-designed surgical guides offer increased accuracy during procedures, while 3D printed instruments can be tailored to specific needs, enhancing surgical efficiency.
- Prosthetics: The ability to create customized prosthetics with complex designs is improving patient comfort, fit, and function.
Applications in Various Surgical Disciplines
3D printing technology has rapidly gained traction in the healthcare sector, particularly in the realm of surgical planning. This revolutionary technique enables surgeons to create highly accurate anatomical models tailored to individual patient needs, which can substantially enhance surgical outcomes across various disciplines, including orthopedic, cardiovascular, and neurosurgery.
In orthopedic surgery, 3D printing is utilized to fabricate patient-specific models that reflect the unique bony structures and deformities. For instance, a case study involving total knee arthroplasty highlighted how surgeons used a 3D-printed model to practice the procedure before the actual operation. This not only allowed for better preoperative planning but also improved the alignment and fit of the prosthetic implant, ultimately leading to enhanced recovery times and patient satisfaction.
Similarly, in cardiovascular surgery, 3D surgical planning and 3D printing plays a critical role in pre-surgical assessments. Surgeons can produce detailed models of cardiac structures based on imaging data, allowing for a deeper understanding of complex anatomies. A notable example includes a pediatric case where 3D-printed aorta models aided in the planning of surgery for congenital heart defects. The printed models facilitated better visualization and coordination among the surgical team, thus improving surgical precision and minimizing risks during the operation.
Neurosurgery is another field that has experienced significant benefits through the application of 3D-printed models. For example, 3D models of skulls have been employed to simulate cranial procedures. In one specific case, a surgeon utilized a 3D-printed model to rehearse the removal of a tumor, leading to a reduction in surgery time and improved postoperative outcomes for the patient. This practice underscores the relevance of 3D surgical planning and 3D printing in fostering precision in complex surgical interventions across multiple disciplines.
Enhanced Training and Education
The integration of 3D printing technology into medical education and surgical training has significantly revolutionized the ways in which future surgeons and healthcare practitioners learn their craft. Traditional teaching methods often struggle to convey complex anatomical structures and surgical procedures, yet 3D-printed models provide a tangible solution. These models can be customized to replicate specific patient anatomies, thereby allowing medical students and residents to gain a deeper understanding of various conditions and the intricate details involved in surgical interventions.
One of the crucial benefits of using 3D-printed models is the facilitation of hands-on learning experiences. Unlike traditional cadaveric dissections, which can be limited in scope or access, 3D models are more readily available and can be repeatedly used for practice without ethical concerns. This accessibility enables learners to explore numerous scenarios and techniques in a safe environment, thus enhancing their confidence and dexterity before they enter an operating room. Furthermore, the ability to study complex structures in a three-dimensional format allows for better spatial awareness, which is vital during actual surgical procedures.
Medical institutions are beginning to recognize the effectiveness of 3D printing technology in the curricula. Many programs are adopting these innovative training tools to prepare students for the rigors of the profession. By familiarizing learners with the surgical approaches they will later implement in real-life settings, educators are ultimately bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. As training evolves, 3D-printed models continue to prove invaluable, optimizing the educational experience while also enhancing the quality of patient care in the long term.
The Future of 3D Printing in Healthcare
The potential of 3D printing in healthcare is vast. Researchers are exploring the use of bioprinting to create functional tissues and organs, potentially addressing organ donor shortages and revolutionizing transplant surgeries.

The Role of Software and Technology
The integration of software and technology has been pivotal in enhancing the effectiveness of 3D printing within the realm of surgical planning. One of the most significant advancements is the improvement in imaging technologies, such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans. These technologies provide highly detailed, three-dimensional images of patients’ anatomy, allowing for the precise mapping of surgical sites. When coupled with advanced imaging software, healthcare professionals can now create detailed digital models that are essential for preoperative planning.
Furthermore, specialized design software plays a crucial role in the customization of surgical models. Programs such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design) enable surgeons and engineers to manipulate the digital representations of anatomical structures easily. This capability not only enhances the accuracy of the models, but it also facilitates the simulation of various surgical approaches. As a result, surgeons can evaluate potential outcomes and choose the most effective techniques prior to entering the operating room, ultimately improving patient safety and surgical efficacy.
In addition to imaging and design software, the evolution of 3D printing materials has significantly contributed to the reliability of surgical models. The availability of biocompatible and durable materials allows for the production of models that closely mimic the properties of human tissues. For instance, silicone, PLA (Polylactic Acid), and resin can be tailored to replicate bone and soft tissue characteristics, ensuring that the 3D surgical planning, 3D printing and 3D-printed models provide realistic tactile feedback during surgical practice. These advancements have led to a higher level of confidence among surgeons when executing complex procedures.
The synergy of advanced imaging technologies, design software, and innovative materials is undeniably reshaping the landscape of surgical planning through 3D printing. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will further enhance surgical outcomes, paving the way for a new standard in personalized healthcare solutions.
Regulatory Considerations and Challenges
The proliferation of 3D printing technologies in healthcare has significantly altered the dynamics of surgical planning, however, it also presents a unique set of regulatory considerations and challenges. Regulatory bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, play a critical role in overseeing the use of 3D printed medical devices and models. These entities are tasked with ensuring patient safety and the effectiveness of technology that is increasingly customizable and complex.
One of the foremost challenges in the regulatory landscape is the classification of 3D printed models. Depending on their intended use, 3D printed items may be classified as medical devices, which can subject them to stringent regulations. For example, models created for preoperative planning that directly influence surgical methods may require extensive documentation to demonstrate they meet the necessary safety and efficacy standards. This process can be both time-consuming and resource-intensive for manufacturers and healthcare providers.
Additionally, the variability inherent in 3D printing processes leads to further complications. Each printing run can yield variations, and the materials used must be verified for biocompatibility and safety. Customization of models tailored to individual patients raises questions about standardization and quality control. Healthcare providers must ensure that the 3D printed products they utilize comply with established guidelines to mitigate the risk of complications during procedures.
Compliance with safety standards is of paramount importance. Healthcare providers and manufacturers are urged to maintain transparent records of the printing process, materials used, and outcomes associated with 3D printed models. As the technology continues to evolve, ongoing collaboration between regulatory authorities, healthcare industries, and researchers will be critical in addressing these challenges effectively. With a structured approach to regulation, the benefits of 3D printing in surgical planning can be realized while safeguarding the health and safety of patients.
3D surgical planning and 3D printing: A Transformation for Patients and Medical Professionals
3D printing is undeniably revolutionizing healthcare. By offering personalized solutions, improved planning, and enhanced surgical techniques, this technology is leading to better patient outcomes, shorter recovery times, and a new era of medical care.
Future Trends in 3D Printing and Surgery
The integration of 3D printing into surgical planning has already demonstrated significant advancements, and the future holds promising potential for further evolution in this field. As technology progresses, we can anticipate innovations that will expand the capabilities of 3D printing, particularly concerning patient-specific surgical models, prosthetics, and even bioprinting organs. The continued development of advanced materials is a key focus area; new composites and bio-compatible substances are being researched to offer improved durability, flexibility, and integration with human tissue.
In the realm of surgical planning, we foresee an increasing reliance on personalized models created from a patient’s unique anatomical data. These custom 3D-printed replicas facilitate enhanced preoperative visualization, allowing surgeons to better understand complex cases and refine their strategies before entering the operating room. Emerging materials will enable these models to simulate various properties, such as bone density or tissue softness, contributing to more precise planning and reduced intraoperative surprises.
Moreover, technological improvements in 3D printing machinery are anticipated. High-resolution printers and faster production times will empower surgical teams to produce more complex geometries, which is crucial for intricate procedures. The introduction of multi-material printing techniques could allow for the development of hybrid models combining both rigid and flexible components, enhancing the realism of surgical simulations.
Ongoing research initiatives focused on bioprinting are also expected to reshape the landscape of surgical interventions. By utilizing 3D printing to create viable tissues and organs, the field could progress towards reducing the dependency on donor organs and enhancing regenerative medicine approaches. This shift could lead to more personalized healthcare solutions, effectively revolutionizing patient outcomes and surgical success rates.
In summary, the future of 3D surgical planning and 3D printing in surgical planning promises an array of advancements fueled by ongoing research, innovative materials, and technology improvements. These developments signify a transformative shift in how surgeries are prepared for, ultimately improving the efficiency and efficacy of surgical procedures.
Conclusion: Embracing the Change
As we have explored throughout this blog post, the integration of 3D surgical planning and 3D printing into surgical planning signifies a transformative leap in the healthcare sector. This technology offers unprecedented opportunities for enhanced precision, customization, and efficiency in surgical procedures. By allowing medical professionals to create patient-specific models, 3D printing removes many of the ambiguities associated with traditional methods of surgical preparation. These advancements not only mitigate risks but also foster improved communication among surgical teams, ultimately contributing to better patient outcomes.
Furthermore, embracing 3D printing encourages a culture of innovation in healthcare. Professionals who actively engage with these technologies can expand their understanding and capabilities, leading to continuous improvements in practice. The ability to visualize complex anatomical structures and rehearse surgical pathways before entering the operating room paves the way for more strategic interventions. This enables surgeons to plan with a level of detail and foresight that was previously unattainable.
The significance of keeping pace with technological advancements cannot be overstated. As healthcare continues to evolve, staying informed about innovations like 3D surgical planning and 3D printing is imperative for all professionals within the field. This will ensure that the benefits of these advancements reach their full potential, sparking further developments in surgical techniques and patient care methodologies. The future of healthcare is undoubtably leaning towards the adoption of cutting-edge technologies, and it is vital for practitioners to embrace this change. By doing so, they will inherently contribute to a safer, more effective healthcare system, ultimately benefiting patients and practitioners alike.
Looking for more information on 3D printing in healthcare?
Search for terms like “3D printed medical models” or “bioprinting in medicine” to explore this exciting field further. Visit our website for further details Cure with 3D.