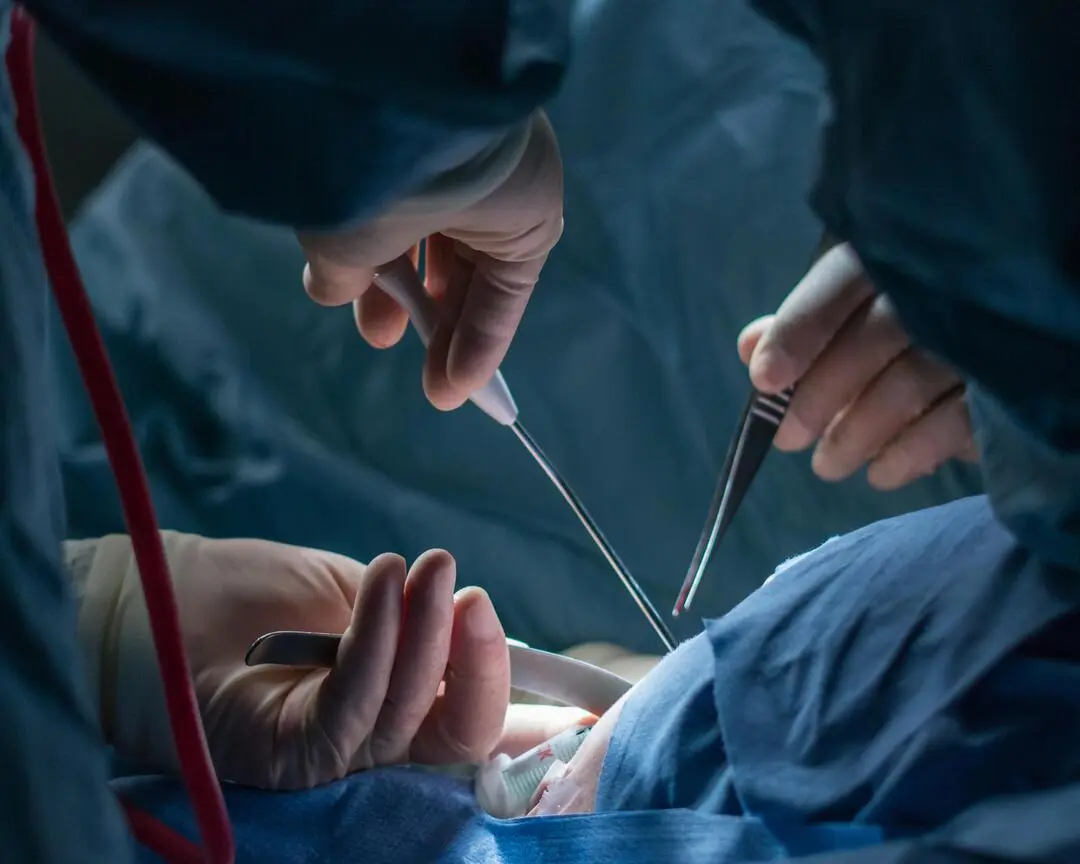
A world where surgery is not just about fixing but also making something different. Fast advancements of technology in surgery are changing the land and establishing a future full of innovating breakthroughs-from tailored-made implants to bio-printed organs.
Beyond Scissors and Sutures: How 3D Printing Emerges in Surgical Equipment.
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that has significantly influenced various fields, including healthcare and surgery. This method involves creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file, primarily by adding material layer by layer. The inception of 3D printing dates back to the early 1980s when Charles Hull developed a technique known as stereolithography. Since then, the technology has evolved substantially, leading to advanced applications in diverse sectors, particularly in the medical industry.
The integration of 3D printing into surgical practices marks a monumental shift from traditional techniques. In conventional surgery, medical professionals often rely on standardized tools and models that may not account for individual patient anatomy. This can limit the effectiveness of surgical interventions and the overall patient outcomes. However, with the advent of 3D printing, surgeons now have the capability to create patient-specific models and surgical tools tailored precisely to the anatomical requirements of each individual. This personalized approach enhances precision during procedures and enhances the effectiveness of surgical planning.
Modern surgical practices are increasingly shaped by advancements in 3D printing technology, which offer numerous benefits. For instance, this technology enables the rapid creation of anatomical models that facilitate better preoperative planning. By visualizing the complex structures of a patient’s anatomy, surgeons can assess potential challenges and strategize accordingly. Furthermore, 3D-printed surgical guides and implants provide a level of accuracy that was previously unattainable, thereby improving overall surgical outcomes. Additionally, the use of biocompatible materials in 3D printing has opened new avenues for reconstructive surgery and tissue engineering.
As 3D printing continues to mature and its applications in surgery expand, it is evident that this technology holds transformative potential in enhancing the quality and efficiency of surgical interventions. The seamless integration of 3D printing into surgical practices is paving the way for a future where precision, personalization, and improved patient care are at the forefront of medical innovation.
Table of Contents
Beyond Scalpels and Sutures: The Rise of 3D Printed Surgical Tools
Customized Cutting Guides: 3D printed cutting guides offer unmatched levels of precision for surgery – this ensures that the placement of implants is apt or causes minimal damage to tissues during intricate procedures.
Patient-Specific Instrumentation: 3D printed instruments may be constructed in accordance with the anatomy of a patient – this can benefit surgery both in terms of efficiency while requiring fewer manipulations.
Bioprinting for Tissue Regeneration: Bioprinting in tissues and organs permits researchers to design functional tissues and organs, without the need for organ transplant in the future.
Current Applications of 3D Printing in Surgery
3D printing technology has significantly advanced the field of surgery, demonstrating its versatility across various disciplines including orthopedics, neurosurgery, and reconstructive surgery. By creating patient-specific models and implants, 3D printing enhances the precision and efficacy of surgical procedures, leading to improved patient outcomes. One prominent application is found in orthopedics, where customized implants and surgical guides tailored to an individual’s anatomy revolutionize the approach to joint replacement. For instance, a recent case study illustrated how a 3D-printed titanium implant was utilized to replace a patient’s damaged femur, enabling a more accurate fit and minimizing recovery time.
In neurosurgery, the ability to produce intricate, patient-specific replicas of brain structures plays a crucial role in complex surgeries. Surgeons can meticulously plan their approach by studying these models, which allow for enhanced preoperative visualization. A notable example is the use of 3D-printed patient skull models that assist in surgeries to remove tumors or correct craniosynostosis. These models help to mitigate surgical risks and facilitate better outcomes, reducing complications associated with unexpected anatomical challenges during surgery.
Reconstructive surgery also benefits from the innovations in 3D printing, particularly in the creation of tissue scaffolds and facial implants. Surgeons are now able to produce personalized facial reconstructive implants that match the contours of a patient’s face. One prominent case involved a patient who suffered severe facial trauma; a custom 3D-printed implant allowed for restoration of natural appearance and function, significantly enhancing the quality of life. Throughout these applications, the significance of 3D printing in surgery is abundantly clear, showcasing its potential to transform traditional surgical practices into highly personalized and precise interventions.
Revolutionizing Pre-Surgical Planning: A Glimpse into the Patient
It is transforming pre-surgical planning altogether:
Anatomical Models: The highly life-like 3D-printed replicas of a patient’s organs or bones enable surgeons to plan procedures quite carefully, practice complex maneuvers before surgery, and improve communication with patients.
Virtual Reality Integration:3D model integration into virtual reality can produce an immersive simulation, making it possible for surgeons to carry out virtual rehearsals of surgeries in a risk-free environment.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Surgical Procedures
The integration of 3D printing into surgical procedures has revolutionized the landscape of modern medicine, offering numerous benefits that enhance both the efficiency of surgeries and the overall patient experience. One of the most significant advantages is the ability to create customized surgical models and implants tailored to the unique anatomy of each patient. This customization allows surgeons to plan and enhance their approach, leading to improved precision during the operation.
Moreover, 3D printing facilitates an intricate understanding of complex anatomical structures, which can be particularly advantageous in challenging cases. Surgeons can practice on these models prior to the actual surgery, allowing for better preparation and a reduction in surprises during the procedure. This not only minimizes the risks associated with surgical complications but also contributes to reduced operation times, enabling healthcare professionals to focus their efforts on delivering care more effectively.
Enhanced patient outcomes are another key benefit stemming from the use of 3D printing in surgical procedures. By providing patients with anatomically accurate models, medical professionals can better educate them about their conditions and the surgical processes involved. This engagement fosters a sense of confidence and understanding, as patients are actively involved in discussions regarding their treatment options. Furthermore, the integration of 3D printed implants can lead to faster recovery times and improved integration with the body, further enhancing the quality of care provided.
In summary, the adoption of 3D printing in surgical processes has significant implications for customization, precision, operational effectiveness, and patient education. By improving surgical planning and facilitating better outcomes, 3D printing stands as a transformative tool in the field of surgical innovation, promising a future filled with advanced capabilities and enhancements in patient care.
Personalized Care: A Paradigm Shift in Surgery
It brings about a new era of personalized care:
Customized Implants: 3D printing is used to create implants that match the anatomy of a given patient perfectly, thereby offering a good fit, better performance, and more rapid recovery periods.
Reduced Surgical Risks: Pre-planning and customization reduce surgical risks from bleeding, infection, and complications.
Improved Patient Outcomes: Because of personalization, precision, and efficiency in treatment the patient outcomes would thus be much better, hence a rather quicker return to normalcy.

Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing in Surgery
Despite the promising advancements in 3D printing technology, several challenges and limitations continue to impede its widespread adoption within the surgical community. One significant hurdle is the regulatory approval process. Medical devices, including 3D printed components, must undergo stringent evaluation to ensure safety and efficacy. This can lead to lengthy delays, affecting the timely implementation of innovative solutions. Regulatory bodies are still adapting to the rapid pace of technological advancements, often resulting in uncertainty regarding compliance requirements for 3D printed surgical tools and implants.
Another limitation lies in the materials currently available for 3D printing. While there has been progress in developing biocompatible materials, options remain limited in terms of strength, durability, and tissue compatibility. Specific surgical applications demand specialized materials that can withstand physiological conditions, which are not yet fully realized in existing 3D printing technologies. Furthermore, there is an ongoing need to enhance the range of materials suitable for various surgical applications, from soft tissue to hard bone structures.
Cost factors also present a significant challenge. The initial investment required for 3D printing technologies can be substantial, particularly for surgical facilities wishing to integrate these systems into their practice. The recurring costs of high-quality materials, maintenance of printers, and potential need for specialized staff can deter many healthcare institutions from adopting this technology. Additionally, insurance reimbursement policies for 3D printed surgical solutions are still evolving, introducing further financial uncertainty.
Finally, effective utilization of 3D printing in surgery necessitates specialized training for surgeons and their teams. Understanding the intricacies of 3D modelling and printing processes is essential for optimal results. As a result, educational programs aimed at equipping surgeons with the necessary skills must be developed to overcome this barrier, ensuring that practitioners are prepared to harness the full potential of 3D printing technologies in surgical innovation.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
The rapid advancements in technology have played a pivotal role in the integration of 3D printing into surgical practices. Recent developments in printing materials, such as biocompatible polymers and advanced metal alloys, have enabled the production of surgical implants and tools that are not only precise but also safe for long-term use within the human body. These innovations provide surgeons with the ability to create personalized prosthetics and implants that match the unique anatomy of individual patients, ultimately improving surgical outcomes.
In addition to new materials, software technology is revolutionizing how surgical models are designed and created. Sophisticated modeling software allows for the precise digital rendering of complex anatomical structures derived from medical imaging data. Surgeons can utilize these three-dimensional models for preoperative planning, providing a better understanding of the surgical landscape before entering the operating room. This pre-surgical approach reduces complications and enhances the overall efficiency of operations.
The evolution of printing techniques, including advancements in multi-material printing and additive manufacturing, further enhances the capabilities of 3D printing within surgery. Techniques such as selective laser sintering and fused deposition modeling allow for the layering of materials to create varied density and flexibility in surgical components. Such flexibility means that surgeons can expect tailored solutions for different surgical scenarios, which can increase the effectiveness of procedures.
Interdisciplinary collaborations among engineers, medical professionals, and material scientists are driving this wave of innovation. By working together, these experts can share knowledge and insights that result in cutting-edge solutions to common challenges in surgery. This collaborative approach ensures that technological advancements are not only innovative but also aligned with clinical needs, thus paving the way for a future where 3D printing becomes commonplace in surgical practices.
The Evolving Landscape: What Lies Ahead in 3D Printing and Surgery?
The future of 3D printing in surgery is quite bright:
Advanced Biomaterials: New biocompatible materials with enhanced properties are constantly being developed for the bioprinting of tissues and organs.
Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI powered surgical robots, equipped with integration using 3D-printed tools, can offer even greater precision and automation in surgery.

Future Trends in 3D Printing for Surgery
As we look ahead to the future of surgical practices, 3D printing is poised to revolutionize various aspects of surgical methods and patient care. One prominent trend that is gaining significant traction is bioprinting, which aims to create complex, viable tissues and organs using living cells. The potential implications of bioprinting for transplantation and regenerative medicine are profound, as it offers the promise of customized tissues that could reduce the risk of rejection and improve recovery outcomes.
Another emerging trend is the increasing emphasis on personalized medicine. Through the use of advanced 3D printing technologies, surgeons can create tailored implants and prosthetics that are designed to meet the unique anatomical needs of each patient. This level of personalization can lead to better fitting devices, improved functionality, and enhanced patient satisfaction. Additionally, the capacity to produce surgical models that accurately reflect a patient’s specific condition allows for improved surgical planning and skill development, reducing operational risks during actual procedures.
Furthermore, advancements in regulatory frameworks are expected to play a crucial role in the adoption of 3D printing in surgical practices. Regulatory bodies are gradually recognizing the need for guidelines that address the complexities of 3D printed medical products. As these frameworks evolve, they will likely provide clearer pathways for the approval and use of custom implants and bioprinted tissues, thereby fostering innovation while ensuring patient safety. Enhanced collaboration between regulatory authorities and medical professionals will be essential to navigate this rapidly evolving field.
Expert predictions indicate that the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning with 3D printing technologies will further augment surgical innovations. This convergence will enable more precise modeling and predictive analytics, leading to improved surgical outcomes. In conclusion, the evolving landscape of 3D printing in surgery holds immense potential for transforming surgical practices, ultimately enhancing the quality of patient care.
Global Perspectives and Case Studies
The adoption of 3D printing technology in surgical innovation has gained momentum across various countries, reflecting a global interest in enhancing healthcare outcomes. Each region is leveraging this technology in unique ways, driven by local needs and available resources. In the United States, for instance, hospitals are increasingly utilizing 3D printing to create patient-specific implants and models, allowing for more tailored surgical procedures. A notable case study from a leading medical institution showcased the successful use of 3D-printed cranial implants that significantly reduced surgery time and improved recovery rates.
In Europe, hospitals in the United Kingdom have pioneered the use of 3D printing for preoperative planning and surgical rehearsal. One remarkable instance involved a complex spinal surgery where surgeons used a 3D-printed model of the patient’s spine to practice the procedure beforehand. This advanced preparation not only enhanced the surgical team’s confidence but also resulted in fewer intraoperative complications. Such cases underscore the critical role that 3D printing plays in refining surgical techniques and improving patient safety.
On the other hand, in countries with emerging healthcare systems, such as India, 3D printing is being adopted to address the pressing demand for affordable medical solutions. A healthcare startup successfully implemented 3D printing to manufacture orthopedic implants at a fraction of the cost of traditional alternatives. This initiative not only democratized access to high-quality surgical interventions but also spurred local innovation in biotechnology.
In South America, Brazil has embraced 3D printing for reconstructive surgeries, highlighting its versatility in addressing complex anatomical challenges. A case study revealed how surgeons utilized this technology to rebuild facial structures following traumatic injuries, showcasing the humanitarian impact of 3D printing in restoring quality of life for patients.
As these diverse examples indicate, the global landscape of 3D printing in surgery is rich with innovation, adaption, and success stories. Each case study emphasizes the technology’s potential to revolutionize surgical practices, underscoring the commitment of healthcare systems around the world to harness its benefits for improved patient care.
A Future Filled with Possibilities: 3D Printing Reimagines Surgery
The advantage of surgical innovation brings with it the advent of 3D printing technology, where “there’s a new level of customization; accuracy; and efficiency,” to mean near-future surgery which would be less invasive and more personalized, the way it leads patients to better outcomes. Possibility in the operating room is limitless.

Ethical Considerations in 3D Printing
The advent of 3D printing technology in the field of surgery has heralded numerous benefits, including personalized implants and advanced surgical models. However, this innovation also raises significant ethical concerns that must be addressed to ensure responsible practice. One of the foremost considerations is patient consent. Surgeons must ensure that patients are fully informed about the use of 3D-printed devices in their procedures. Transparency in communicating the benefits, risks, and potential uncertainties surrounding these technologies is essential in fostering trust and promoting shared decision-making between patients and healthcare providers.
Data privacy is another critical ethical issue associated with 3D printing in surgery. The creation of customized medical devices or implants often requires detailed anatomical data from patients. This sensitive information must be protected against unauthorized access and misuse. Establishing stringent protocols for data handling and storage is vital in safeguarding patient privacy. Surgeons and manufacturers share the ethical responsibility of ensuring compliance with regulations governing personal health information, thereby maintaining the integrity of patient data throughout the 3D printing process.
Moreover, ethical considerations extend to the responsibilities of surgeons and manufacturers involved in 3D printing. Surgeons are obliged to assess the quality and safety of 3D-printed products before their application in surgery. This necessitates rigorous evaluation of the materials used and adherence to established medical standards. Manufacturers, on the other hand, must approach the production of 3D-printed medical devices with a commitment to ethical supply chain practices, ensuring that the processes from design to delivery uphold the highest standards of patient safety and welfare.
As the integration of 3D printing in surgical practice continues to expand, the ethical implications surrounding its use must remain at the forefront of discussions. Addressing these concerns is essential for ensuring that this remarkable technology contributes positively to patient care while upholding the values of ethical medical practice.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Surgery
In recent years, 3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary technology with the potential to significantly transform the landscape of surgical practice. The integration of this innovative technique into surgical procedures has demonstrated remarkable benefits, including enhanced precision and customization of surgical tools and implants tailored specifically to individual patients. As surgeons and medical professionals increasingly adopt this technology, it becomes evident that 3D printing is not merely a trend but rather a substantial paradigm shift poised to improve clinical outcomes.
The ability to create patient-specific models through 3D printing has proven invaluable in preoperative planning and education. Surgeons can better visualize complex anatomies and rehearse intricate procedures prior to actual surgery. This preparation not only aids in minimizing errors but also contributes to increased confidence among surgical teams, ultimately benefiting patient safety. Furthermore, the rapid prototyping capabilities of 3D printing allow for real-time adjustments and optimizations during surgical interventions, thereby streamlining operations and reducing overall procedural time.
Moreover, the accessibility of 3D printing technology holds promise for enhancing healthcare delivery, particularly in underserved regions. The capability to produce affordable, custom medical solutions could bridge existing gaps in surgical care, ensuring that all patients receive high-quality treatment irrespective of geographical limitations. Consequently, as 3D printing continues to evolve, it becomes imperative for healthcare professionals to embrace its potential and remain informed about the latest advancements. Continued support for research and development in the field will be crucial in driving further innovations and unlocking even greater possibilities for future surgical practices.
In conclusion, the transformative potential of 3D printing in surgery cannot be understated. By enhancing patient care and surgical efficiency, this technology sets the stage for a new era in medicine. It is essential for stakeholders across the medical community to engage with these advancements and champion ongoing innovations in 3D printing, ensuring that the future of surgery is optimized for both practitioners and patients alike.
Ready to explore the exciting world of 3D printing in surgery?
Search for terms like “3D printed bioprinting for organ regeneration” or “benefits of 3D printed surgical guides” to delve deeper into this groundbreaking field and its impact on the future of healthcare.